os211
Top 10 List of Week 07
-
Petersons algorithm
Petersons Algorithm is used to synchronize two processes. It uses two variables, a bool array flag of size 2 and an int variable turn to accomplish it. In the solution i represents the Consumer and j represents the Producer. Initially the flags are false. When a process wants to execute its critical section, it sets its flag to true and turn as the index of the other process. This means that the process wants to execute but it will allow the other process to run first. The process performs busy waiting until the other process has finished its own critical section. -
Semaphores in Operating System
Semaphores are integer variables that are used to solve the critical section problem by using two atomic operations, wait and signal that are used for process synchronization.
-
Deadlock Characterization
Deadlock characterization describes the distinctive features that are the cause of deadlock occurrence. Deadlock is a condition in the multiprogramming environment where the executing processes get stuck in the middle of execution waiting for the resources that have been held by the other waiting processes thereby preventing the execution of the processes.In this website, we will discuss the characteristics that are essential for the occurrence of deadlock. The four conditions that must sustain at the same time to eventuate a deadlock are: mutual experience, hold and wait, no preemption, circular wait. -
Bankers Algorithm in Operating System
The bankers algorithm is a resource allocation and deadlock avoidance algorithm that tests for safety by simulating the allocation for predetermined maximum possible amounts of all resources, then makes an s-state check to test for possible activities, before deciding whether allocation should be allowed to continue. -
Race Condition
A race condition is a situation that may occur inside a critical section. This happens when the result of multiple thread execution in critical section differs according to the order in which the threads execute. Race conditions in critical sections can be avoided if the critical section is treated as an atomic instruction. Also, proper thread synchronization using locks or atomic variables can prevent race conditions.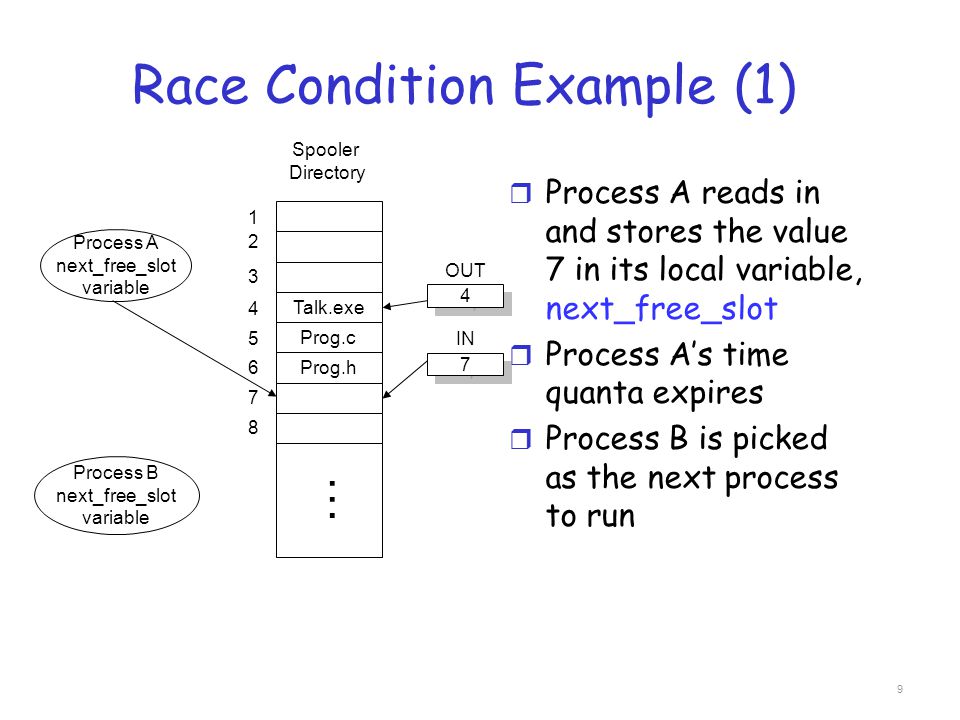
-
Bounded-Buffer Problems
The bounded-buffer problems (aka the producer-consumer problem) is a classic example of concurrent access to a shared resource. A bounded buffer lets multiple producers and multiple consumers share a single buffer. Producers write data to the buffer and consumers read data from the buffer.A bounded buffer with capacity N has can store N data items. The places used to store the data items inside the bounded buffer are called slots. Without proper synchronization some errors may occur such as : the producers doesnt block when the buffer is full, two consumers reads the same slot, and a consumer consumes an empty slot in the buffer.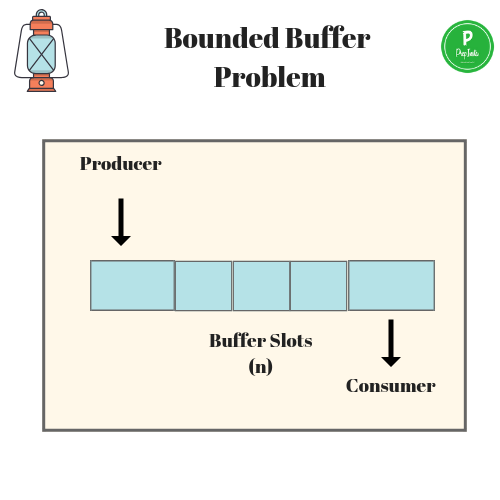
-
What is MyShare and OpenShare?
On the Network drive, home users will have two separate spaces to store their files. MyShare is a private share, which is password protected. Only the admin user can read and write files in it. OpenShare is a public directory on the local network, which can be read and written (thus including delete files/folder) by everyone who has access to the local network. -
Deadlock Avoidance
In deadlock avoidance, the request for any resource will be granted if the resulting state of the system doesn’t cause deadlock in the system. The state of the system will continuously be checked for safe and unsafe states. In order to avoid deadlocks, the process must tell OS, the maximum number of resources a process can request to complete its execution. The simplest and most useful approach states that the process should declare the maximum number of resources of each type it may ever need. The Deadlock avoidance algorithm examines the resource allocations so that there can never be a circular wait condition. -
The Critical Section Problem
Critical Section is the part of a program which tries to access shared resources. That resource may be any resource in a computer like a memory location, Data structure, CPU or any IO device. The critical section cannot be executed by more than one process at the same time; operating system faces the difficulties in allowing and disallowing the processes from entering the critical section. The critical section problem is used to design a set of protocols which can ensure that the Race condition among the processes will never arise.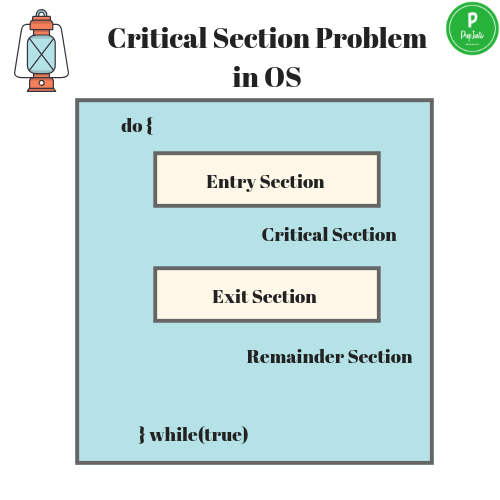
-
Process Synchronization
Process Synchronization is the task of coordinating the execution of processes in a way that no two processes can have access to the same shared data and resources. It is specially needed in a multi-process system when multiple processes are running together, and more than one processes try to gain access to the same shared resource or data at the same time.